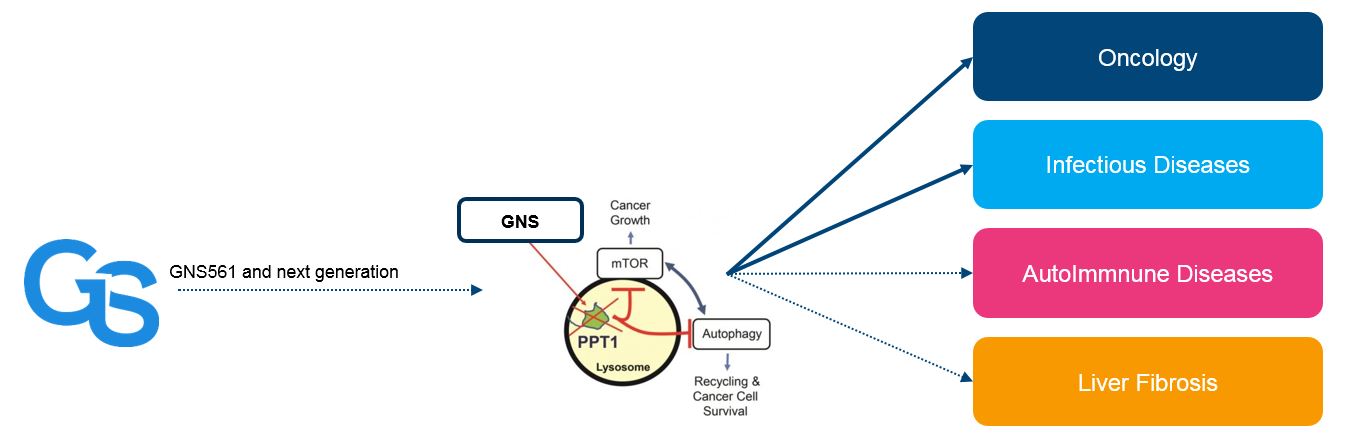
Autophagy is a catabolic process which degrades a cellular own component through the lysosomal machinery. The lysosome, at the heart of the autophagy sytem is important in various processes (cancer, infection…).
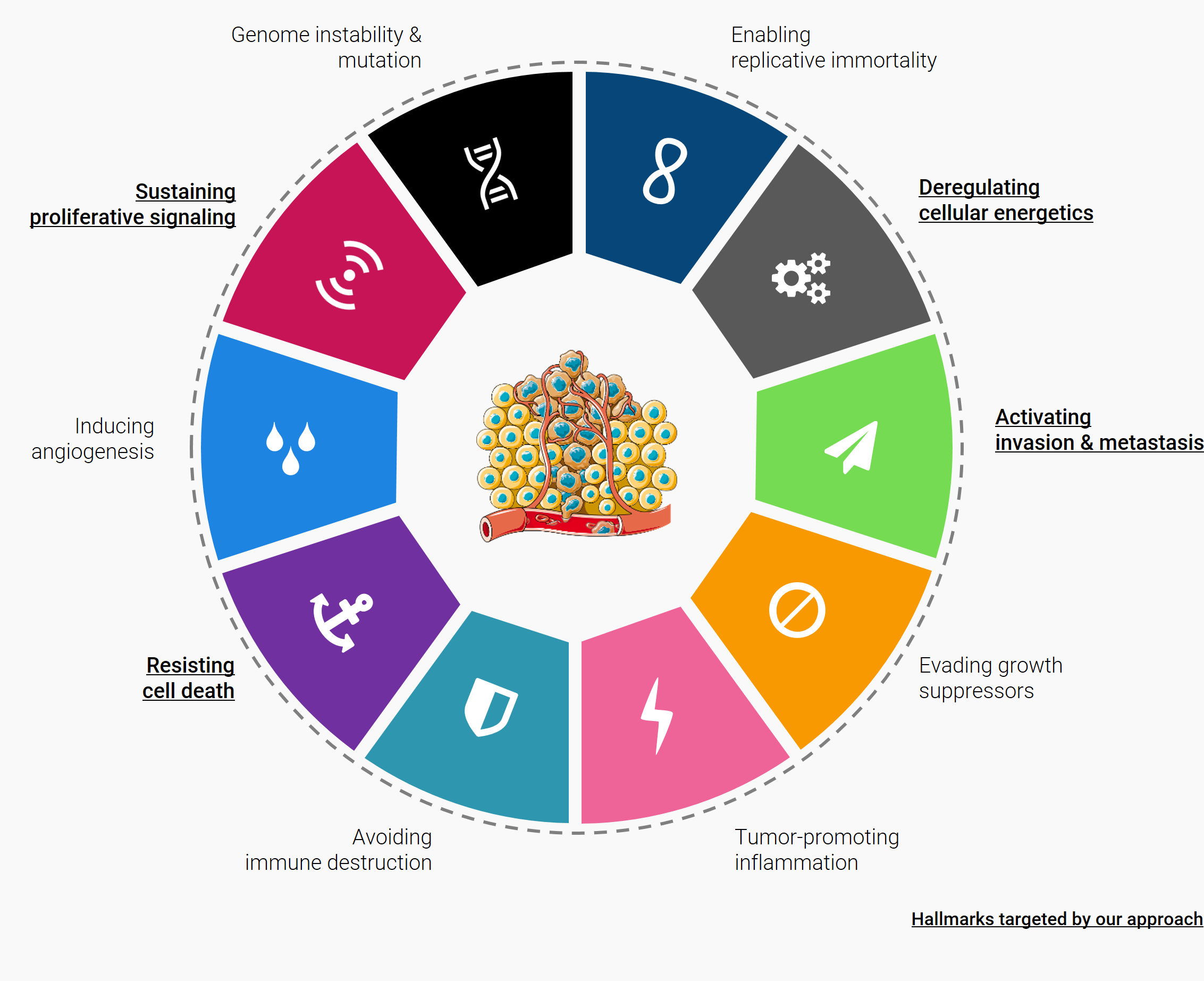
In Cancer, they are required in tumor cells for cellular adhesion, motility and signaling, exocytosis, angiogenesis and overall survival, growth, aggressiveness, metastatic potential and drug resistance. Because of their high metabolic rates, rapidly dividing and invasive cancer cells require increased new biomass production to survive. The lysosome is also important for adaptation to nutrient stress as it contains hydrolytic enzymes that play a major role in the degradation of intracellular macromolecules and catabolic (such as autophagy) and anabolic growth. This busy lysosomal behavior leads to alterations in lysosomal structure and function, which, paradoxically, renders cancer cells more sensitive to lysosomal destabilization. In addition, lysosomal enzyme activity is elevated in many tumors compared to adjacent normal tissue, and several reports suggest that lysosomes in tumor cells are more fragile than normal lysosomes.
Therefore, lysosome seems to be a target of interest in the fight against cancers. Targeting lysosomes triggers apoptotic and lysosomal cell death pathways.
In virology, It has been shown that autophagy is activated during virus and bacterial infection and that some viruses can use the autophagy system to facilitate their own replication . Some viruses, such as Coronaviruses are single stranded, positive sense RNA viruses, which induce the rearrangement of cellular membranes upon infection of a host cell. This provides the virus with a platform for the assembly of viral replication complexes, improving efficiency of RNA synthesis.
In october 2016, Yoshinori Ohsumi received the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. Professor Maria Masucci of the Nobel Assembly described the science behind the prize:
Source: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2016/prize-announcement